Aircraft Components
3. Engines
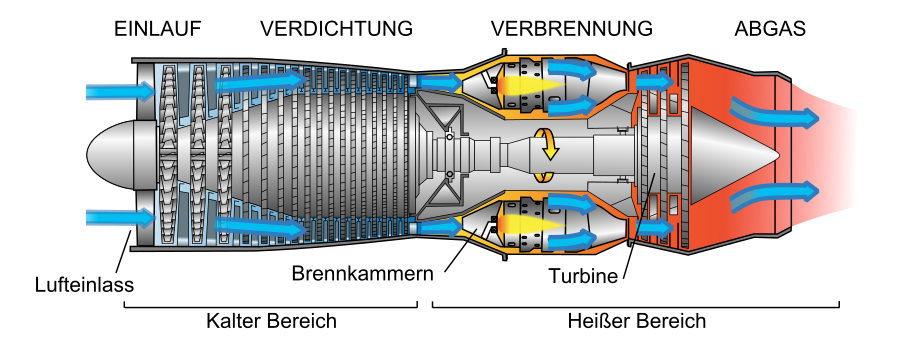 An engine is the power plant of an airplane. This provides the necessary propulsion, i.e. the thrust. An airplane which does not move forward. Usually does not fly.
An engine is the power plant of an airplane. This provides the necessary propulsion, i.e. the thrust. An airplane which does not move forward. Usually does not fly.
Small, light and slow flying aircraft need only small engines. A better lawnmower engine often still serves the purpose today. Typical private airplanes of today or fighter planes from the First World War fly with engines that could well come from a car in terms of performance, and this is often the case. Common for these are from 1,000 ccm with 100 HP up to the thick V8 with 4 liters capacity and 350 HP and more per engine.
Similar to cars, size and weight of an airplane and of course the expected wind resistance at the desired speed determine the necessary propulsion.
Typical engines of today are:
- Piston Engine with propeller (as In-Line or Radial engine, in the past also Rotary engines)
- Jet Engine
- Turboprop (a small jet engine combined with a propeller)
